CBSE CLASS 12 - Biology - CH 5 - Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Important Definitions (#cbseNotes)
Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Important Definitions
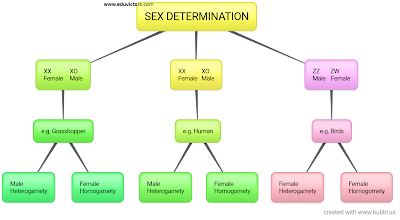
Q1: Define heredity.
Answer: It can be defined as the transmission of characters from one generation to successive generations of living organisms.
Q2: Define Alleles
Answer: The various forms of a gene are called alleles.
Q3: What are multiple alleles?
Answer: If a gene has more than two alleles then they are said to be multiple alleles. e.g. In humans ABO blood groups is an example for multiple allelism.
Q4: What is genotype?
Answer: The genetic constitution of an organism is its genotype.
Q5: What is phenotype?
Answer: The external / observable characteristics of an organism constitute its phenotype.
Q6: What is Pleiotropy?
Answer: The ability of a gene to have multiple phenotypic effects because it influences a number of
characters simultaneously is known as Pleiotropy. Eg: Phenylketonuria.
Q7: Define Homozygote.
Answer: A homozygote is an individual having two copies of the same allele at a locus. OR It is an individual organism in which the members of a pair of alleles for a character are same.
Q8: Define Heterozygote.
Answer: It is an individual organism in which the members of a pair of alleles of a character are different.
Q9: What is polygenic inheritance?
Answer: The cumulative effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character is known as
polygenic inheritance. e.g. skin colour in human beings.
Q10: Define Dominant characters.
Answer: The form of the character which is expressed in the F1 hybrid is called dominant character.
Q11: What is a recessive character?
Answer: The form of the character which is suppressed in the presence of the dominant character: character in a hybrid is called recessive character.
Q12: What is a Monohybrid cross?
Answer: It is a cross between individuals of the same species, in which the inheritance of contrasting pairs of a single trait is considered.
Q13: What is a Dihybrid cross?
Answer: It is a cross between two individuals of the same species, in which the inheritance of contrasting pairs of two traits is considered.
Q14: Define Epistasis.
Answer: Epistasis is the phenomenon where the effect of one gene (locus) is dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes', i.e. phenotypic expression of a gene at one locus alters that of a gene at a second locus.
Q15: What is haplodiploidy?
Answer: It is a mechanism of sex determination. In this system the sex of the off spring is determined by the number of sets of chromosomes. E.g.: Honeybees.
Q16: What is Lyonization?
Answer: Lyonization is a process by which one of two copies of X – chromosome present in the body cells of female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X – chromosome is transcriptionally inactive called heterochromatic body.
Comments
Post a Comment